1. Core Job Submission Commands
These commands launch analyses directly from the command line/terminal, bypassing CAE.
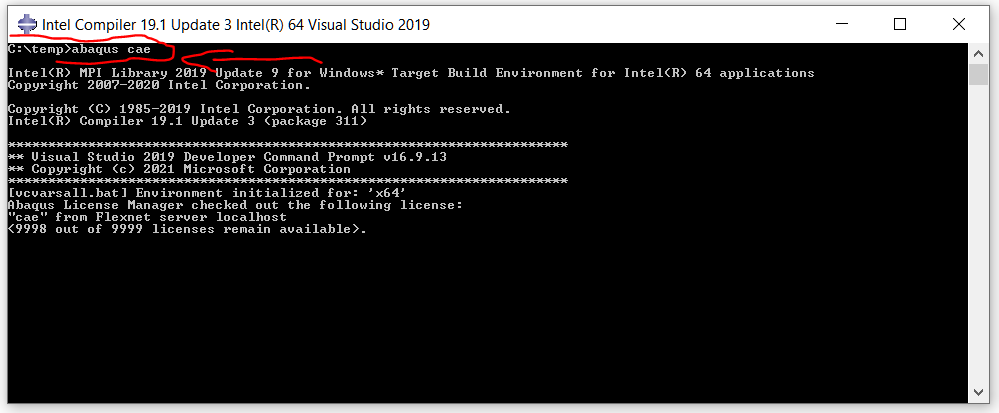
1.1. Standard Job Execution
abaqus job=BRACKET_ANALYSIS # Basic job submission abaqus job=IMPACT cpus=8 # Specify CPU cores abaqus job=THERMAL_MAP memory="4 gb" # Allocate memory abaqus job=ASSEMBLY double interactive # Double precision, interactive mode
1.2. Advanced Execution Controls
abaqus job=MODAL input=model.inp # Specify custom input file abaqus job=FRACTURE user=umat.f # Include user subroutines abaqus job=DYNAMIC oldjob=STATIC # Continue from previous analysis abaqus job=OPTIMIZE scratch="D:\temp" # Set scratch directory
2. Interactive and Debug Execution Modes
Critical for development and troubleshooting workflows.
2.1. Interactive Session Control
abaqus job=Job-1 interactive # Launch with terminal interaction abaqus job=TEST run_wait=NO # Submit and return immediately abaqus job=DEBUG interactive recover # Enter recovery mode abaqus job=BENCHMARK ask_delete=NO # Suppress file deletion prompts
2.2. Debug and Diagnostic Execution
abaqus job=VERIFY datacheck # Data check only (no analysis) abaqus job=CONTACT info=verbose # Verbose contact information abaqus job=PROBLEM_MODEL debug # Enable debug output abaqus information=memory # Check memory requirements
3. Multi-Processing and HPC Execution
Optimize for performance on workstations and clusters.
3.1. Parallel Processing Commands
abaqus job=SOLID parallel # Enable parallel processing abaqus job=LARGE_MODEL cpus=32 mp_mode=threads # Thread-based parallel abaqus job=COMPLEX cpus=12 mp_mode=mpi # MPI-based parallel abaqus job=DOMAIN cpus=24 domain=parallel explicit # Explicit domain parallel
3.2. Cluster and Queue System Commands
abaqus job=HPC_ANALYSIS queue # Submit to default queue abaqus job=OVERNIGHT after=22:00 # Schedule execution time abaqus job=RESUME restart # Restart from interruption abaqus job=BATCH background # Run in background
4. File Management and Utility Commands
Essential for workflow automation and file handling.
4.1. File Conversion and Extraction
abaqus odbreport job=RESULTS # Generate report from ODB abaqus python script=extract.py # Execute Python script abaqus cae noGUI=preprocess.py # Run CAE without GUI abaqus fetch job=REMOTE_JOB # Retrieve results from remote
4.2. Database and Results Management
abaqus upgrade job=LEGACY_MODEL # Upgrade old model database abaqus append job=NEW phase=STRESS # Append results to existing ODB abaqus delete job=TEMP keep=inp # Clean up, keep input file abaqus recover job=CRASHED # Attempt recovery from crash
5. Common Execution Patterns and Scripting
5.1. Sequential Job Execution (Batch Script)
# Windows batch file example abaqus job=STEP1 cpus=4 abaqus job=STEP2 oldjob=STEP1 cpus=4 abaqus job=STEP3 oldjob=STEP2 cpus=4
5.2. Parameter Study Automation
# Python-driven parameter sweep
import subprocess
thickness_values = [1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5]
for i, t in enumerate(thickness_values):
cmd = f'abaqus job=PARAM_{i} user=mat_prop.f thickness={t} cpus=6'
subprocess.run(cmd, shell=True)6. Error Handling and Job Monitoring
6.1. Status Checking Commands
abaqus job=ANALYSIS information=status # Check job status abaqus where job=PROCESSING # Locate running job abaqus suspend job=LONG_RUN # Temporarily suspend abaqus resume job=SUSPENDED # Resume suspended job
6.2. Output and Log Management
abaqus job=JOB redirect=log.txt # Redirect output to file abaqus job=SIMULATION terminal=log.msg # Terminal output to file abaqus job=ANALYSIS echo=NO # Suppress command echo
7. Best Practices for Production Workflows
7.1. Recommended Execution Patterns
# 1. Always test with datacheck first abaqus job=TEST_MODEL datacheck user=umat.f # 2. Production run with full resources abaqus job=FINAL_ANALYSIS cpus=16 memory="32 gb" mp_mode=mpi # 3. Monitor and manage output abaqus job=PRODUCTION interactive redirect=run.log
7.2. Environment and Configuration Commands
abaqus environment # Display environment settings abaqus licensing=info # Check license status abaqus site="C:\abaqus_files" # Set site-specific location abaqus standard_parallel=4 # Set default parallel processes
8. Conclusion: Building Efficient Execution Workflows
Mastering command-line execution transforms sporadic analysis into automated, reproducible workflows. The most effective simulation engineers combine these commands with scripting to create:
- Validation pipelines that automatically test model changes
- Parameter optimization loops that iterate designs
- Results extraction routines that generate reports automatically
- Error recovery systems that handle failures gracefully
The advanced frontier involves integrating these commands with cloud HPC systems using SLURM or PBS pro job schedulers, containerizing Abaqus with Docker for consistent environments, and building full CI/CD pipelines for simulation validation.
Remember: Always include interactive during development for immediate feedback, but remove it for production runs to ensure clean batch execution. Document your execution parameters alongside your model assumptions for complete reproducibility.